What is Product Marketing and How to Use it: A Comprehensive Guide

What is Product Marketing and How to Use it: A Comprehensive Guide
Having a high-quality product is never enough for a business. Where do you want to sell it, and to whom? How do you want to find the right audience for your product? How do you want to present and promote it?
Product Marketing is the process of answering those questions. Without it, it is almost impossible to grow your business or even survive in this highly competitive world. It is a crucial art, especially for Ecommerce businesses that need to stand out in a highly competitive environment.
Whether you’re launching a new product or looking to revamp your existing marketing strategies, understanding the ins and outs of product marketing is crucial. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover everything from the basics of product marketing to creating a winning product marketing strategy.
What Is Product Marketing?
Product marketing is the process of bringing a product to market and promoting it to the right audience with the aim of selling more. It bridges the gap between product development, Marketing, and sales, ensuring that the product meets the target market’s needs and is positioned effectively.
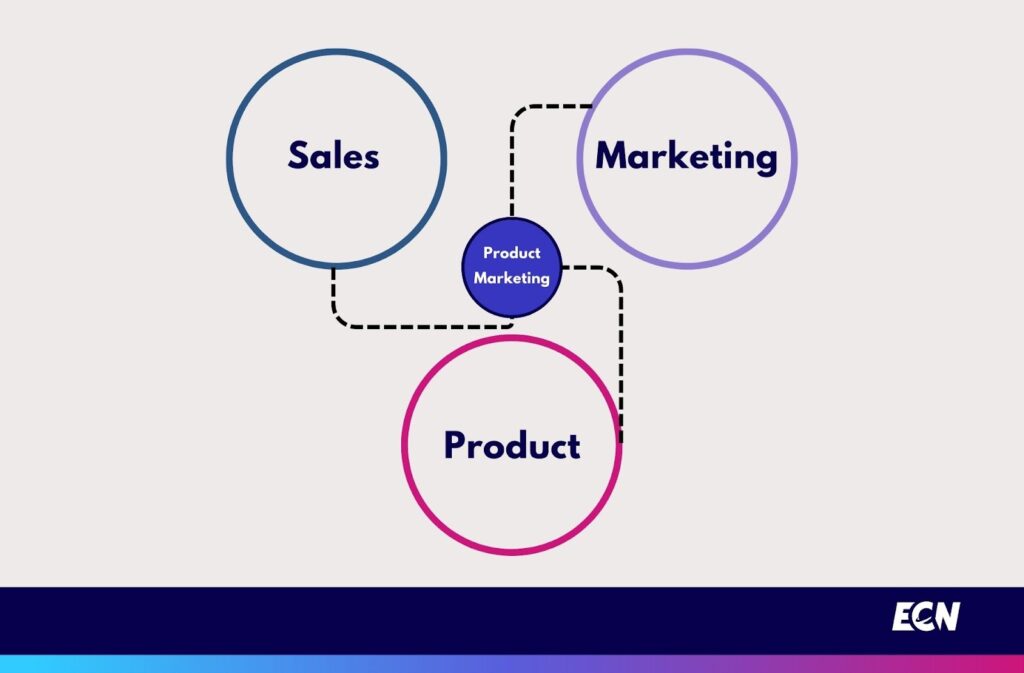
It seems like it is very similar to the general word “Marketing” that we all heard about, right?
However, there are some differences between these concepts. Product marketing is focused on the specific product or service that a business is offering. It involves understanding the needs and wants of the target market, developing a positioning strategy, and creating and executing marketing campaigns that will help to drive sales.
On the other hand, Standard marketing is a broader discipline that encompasses all aspects of marketing, including product marketing, brand marketing, marketing communications, etc. It is concerned with building awareness of a business and its products or services, generating leads, and driving sales.
How To Create A Product Marketing Strategy That Works?
Creating a successful product marketing strategy requires careful planning and execution. By creating a product marketing strategy you will be able to answer the “how to market a product” question.
Here we provided a step-by-step guide that you can use for your product marketing strategy:
1. Market Research
Market research is the foundational step in any successful product marketing endeavor. Here’s what it entails:
- Creating a Protopersona: Start by developing a protopersona, which is a preliminary representation of your ideal customer. While it may not be as detailed as a full persona, it helps you begin to understand your target audience. Consider basic demographics, pain points, and goals.
- Identifying Your Target Audience: Once you have a proto-persona, refine it by collecting data and conducting surveys or interviews with potential customers. This will help you validate and enhance your understanding of your target audience, ensuring that your product aligns perfectly with their needs and preferences.
- Understanding Pain Points: Continue your research by delving into the problems, needs, and pain points your target audience faces. What challenges are they experiencing that your product can solve? This insight will inform your messaging and product positioning.
- Competitor Analysis: Investigate your competitors. What similar products or services are already in the market? What are their strengths and weaknesses? Identifying gaps or opportunities in the competitive landscape is crucial for differentiation.
2. Product Positioning
Product positioning is about defining how your product fits into the market and how it stands out. Here’s what you need to do:
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Determine what makes your product unique. What features, benefits, or qualities set it apart from the competition? Your USP is a key part of your positioning.
- Target Market Alignment: Ensure that your product aligns perfectly with the needs and preferences of your target audience. Your product should be a solution to their pain points.
- Value Communication: Develop a clear and compelling message that communicates the value your product offers. This message should resonate with your target audience and address their specific pain points.
3. Pricing Strategy
Setting the right price for your product is critical for success. Consider the following:
- Cost Analysis: Calculate the production, marketing, and distribution costs associated with your product. Ensure that your pricing covers these costs while allowing for a profit margin.
- Competitive Pricing: Research your competitors’ pricing strategies. Your pricing should be competitive, taking into account what similar products are charging.
- Perceived Value: Consider how your pricing affects the perceived value of your product. Sometimes, a higher price can convey quality and exclusivity.
4. Messaging and Branding
Effective messaging and branding are essential for creating a strong product identity:
- Crafting Compelling Messages: Develop messages that highlight your product’s benefits and its ability to solve your target audience’s problems. Your messaging should be concise, persuasive, and consistent across all marketing channels.
- Brand Identity: Create a cohesive brand identity that reflects your product’s values and resonates with your audience. This includes designing a compelling logo, choosing the right color schemes, and establishing brand guidelines.
- Brand Voice: Determine the tone and voice of your brand. Are you friendly and approachable, or professional and authoritative? Consistency in your brand voice helps build trust.
5. Distribution Channels
Choosing the right distribution channels ensures your product reaches your target audience:
- Online Channels: If you’re in Ecommerce, consider platforms like your website, social media, and third-party marketplaces (e.g., Amazon, eBay).
- Offline Channels: If you have physical stores or partners, ensure your product is available through these channels.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: Ensure efficient and reliable product delivery to customers, both online and offline.
6. Promotion
Promoting your product involves creating marketing campaigns and tactics to generate awareness and interest:
- Content Marketing: Develop valuable content, such as blog posts, videos, or infographics, that educate and engage your audience. Content can also be used for SEO to improve visibility.
- Advertising: Utilize various advertising channels, including online ads, social media ads, and search engine marketing, to reach a wider audience.
- Public Relations: Build relationships with media outlets and influencers to gain positive exposure for your product.
- Email Marketing: Create email campaigns to nurture leads, inform customers about promotions, and build a loyal customer base.
What Is Product Marketing Plan?
A product marketing plan is a detailed document outlining your product marketing strategy, goals, and tactics. It serves as a roadmap for your product’s success, helping you stay on track and measure progress.
Product Marketing Examples
Let’s explore some real-world product marketing examples:
Apple iPhone Launch
Apple’s product marketing for the iPhone is a masterclass in creating anticipation and desire through carefully crafted teasers and keynotes. Let’s analyze the iPhone product launches:
- Background: Apple’s iPhone launch events have become iconic in the tech industry. They typically occur annually and generate massive anticipation worldwide.
- Execution: Apple starts the marketing process well in advance of the actual launch date. They employ various teaser campaigns, which are cryptic and create suspense. These teasers generate curiosity and speculation among consumers and the media.
- Key Features Highlight: During the launch event, Apple’s CEO or other key executives showcase the iPhone’s key features, improvements, and innovations. They use demonstrations and visuals to illustrate how the product works and its impact on users’ lives.
- Media Coverage: Apple invites influential tech journalists, bloggers, and industry insiders to the launch event. This not only ensures significant media coverage but also lends credibility to the product.
- Availability: Apple typically announces the product’s availability shortly after the event, creating a sense of urgency among consumers to be among the first to own the new iPhone.
- Customer Engagement: Apple encourages customers to visit its stores or its website to pre-order the new iPhone immediately after the launch event. This drives early sales and engagement.
- Ongoing Marketing: Apple’s marketing efforts continue well beyond the launch event, with additional advertisements, user testimonials, and promotions to sustain interest and maintain strong sales throughout the product’s lifecycle.
Tesla’s Cybertruck
Tesla’s announcement of the Cybertruck generated massive buzz through social media and its unconventional design.
- Background: Tesla’s Cybertruck launch was notable for its unconventional design and marketing approach. It aimed to disrupt the electric vehicle (EV) and pickup truck markets.
- Execution: Tesla CEO Elon Musk announced the Cybertruck at an event filled with Tesla enthusiasts and media. The design was radically different from traditional pickup trucks, with a futuristic and angular appearance.
- Key Features Highlight: Musk highlighted the Cybertruck’s unique features, including its stainless steel body, bulletproof windows (which had a memorable mishap during the presentation), and impressive performance metrics like acceleration and towing capacity.
- Social Media Buzz: The Cybertruck launch relied heavily on social media. Tesla encouraged pre-orders online, and the event generated significant social media buzz, with millions of mentions and reactions.
- Pre-Order Incentives: Tesla offered incentives for customers to pre-order the Cybertruck, such as early access to vehicle options and discounts.
- Viral Marketing: The bold and polarizing design of the Cybertruck led to countless discussions, memes, and parodies on social media, extending its reach beyond traditional marketing channels.
- Continued Hype: Tesla has kept the Cybertruck in the public eye through periodic updates and production announcements, maintaining interest even as the release date was delayed.
Product Marketing Metrics
In today’s data-driven world, understanding and leveraging metrics are at the core of making informed decisions and achieving desired outcomes. This holds true for product marketing, a pivotal function that bridges the gap between a company’s products and its customers. Metrics in product marketing serve as the compass guiding businesses through the turbulent waters of the market, helping them navigate with precision and confidence.
The most important key metrics to consider include shown below:
- Sales Revenue: Monitor how your product marketing efforts impact sales.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Calculate the cost of acquiring a new customer.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Assess the long-term value of your customers.
- Conversion Rates: Track the percentage of leads that become paying customers.
- Customer Satisfaction: Gather feedback to gauge customer happiness.
- Market Share: Measure your product’s share of the market.
Product-Led Marketing
Product-led marketing (PLM) is a kind of product marketing. However, it is a specific approach to product marketing that focuses on using the product itself as the primary driver of customer acquisition, activation, and retention.
This approach places the product itself at the forefront of marketing efforts, emphasizing its inherent value and utility to attract and retain customers. Product led marketing isn’t just a trend; it’s a strategic shift that offers numerous benefits. It allows companies to align their marketing with the customer’s journey, fosters trust through user experience and encourages organic growth through satisfied customers becoming advocates.
What Is Product Led Marketing
Product-led marketing (PLM) is a go-to-market strategy that focuses on using the product itself as the primary driver of customer acquisition, activation, and retention. This means that the product is used to educate potential customers about its value, to onboard them into the product, and to encourage them to use it regularly.
PLM is a relatively new marketing approach, but it is becoming increasingly popular as businesses look for ways to reduce their reliance on traditional marketing channels, such as advertising and sales. PLM can be a very effective way to grow a business, but it requires a deep understanding of the product and the target market.
Companies like Slack and Dropbox have excelled in this approach by offering freemium models that encourage users to adopt their products organically.
Product Marketing Vs Content Marketing
You are trying to learn about a specific topic, You open a website or download an E-book, and after a few paragraphs, you will see that you are actually reading a guideline book of software or a product. Why? What happened? Well, this happens a lot. When a company gets confused about Product marketing and Content marketing, this is the result.
Therefore, it is important to understand the differences. Product marketing is focused on promoting and selling a specific product or service to potential customers. It aims to demonstrate the value, features, benefits, and uniqueness of your product or service, and persuade customers to buy it.
Content marketing, on the other hand, is focused on creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and engaging content to attract and retain a clearly defined audience. It aims to educate, inform, entertain, and inspire your audience, and build trust and authority for your brand
Product marketing is centered around promoting a specific product, whereas content marketing involves creating and distributing valuable content to attract and engage a target audience. These two disciplines often overlap, with content marketing supporting product marketing efforts. But they should not be used instead of each other.
For example, a blog article’s aim is to help the readers answer their questions, it is not a good place to promote your products directly.
Who is a product marketer?
A product marketer is a professional responsible for strategizing, executing, and analyzing product marketing efforts. They serve as a bridge between the product development team and the sales and marketing teams.
Product marketers are typically based in the marketing department, but they may also work closely with the product development, sales, and customer success teams. They need to have a strong understanding of marketing, product development, and sales in order to be successful.
What are the tasks of a Product marketing manager?
A product marketing manager (PMM) is responsible for the strategic positioning, messaging, and go-to-market (GTM) planning for a product or service. They work with a variety of teams, such as product development, sales, and marketing, to ensure that the product is successful.
Some common tasks of a product marketing manager include:
- Understanding the target market: PMMs need to understand the needs and requirements of the target market in order to create a product that they will want to buy. They do this by conducting market research, analyzing customer data, and talking to potential customers.
- Developing a positioning strategy: PMMs need to develop a positioning strategy that clearly communicates the value of the product to the target market. This includes identifying the product’s unique selling proposition (USP) and developing messaging that resonates with the target market.
- Creating marketing materials: PMMs create marketing materials, such as website copy, blog posts, and social media posts, that communicate the value of the product to the target market. They also work with designers and creatives to develop visual assets, such as logos and product illustrations.
- Running marketing campaigns: PMMs run marketing campaigns to reach the target market and generate interest in the product. This includes developing and executing paid advertising campaigns, social media marketing campaigns, and public relations campaigns.
- Tracking the results of marketing campaigns: PMMs track the results of marketing campaigns to measure their effectiveness and make necessary adjustments. They use data from analytics tools to track things like website traffic, leads generated, and sales.
- Working with product development: PMMs work with product development to ensure that the product meets the needs of the target market. They provide feedback on product features and functionality, and they help to develop the product’s launch plan.
- Working with sales: PMMs work with sales to ensure that the product is effectively sold to customers. They provide sales teams with marketing materials and training, and they help to develop sales strategies.
PMMs are typically based in the marketing department, but they may also work closely with the product development, sales, and customer success teams. They need to have a strong understanding of marketing, product development, and sales in order to be successful.
Here are some of the skills that a product marketer should have:
- Marketing skills: PMMs need to have strong marketing skills, such as copywriting, content marketing, and social media marketing.
- Product development skills: PMMs need to have a basic understanding of product development, such as the product development process and the different stages of product development.
- Sales skills: PMMs need to have a basic understanding of sales, such as the sales process and the different types of sales.
- Communication skills: PMMs need to have strong communication skills, both written and verbal.
- Analytical skills: PMMs need to have strong analytical skills to track the results of marketing campaigns and make necessary adjustments.
Key Insights
- Product marketing is the process of bringing a product to market and promoting it to the right audience with the aim of selling more. It bridges the gap between product development, marketing, and sales, ensuring that the product meets the target market’s needs and is positioned effectively.
- Effective product marketing is vital for business growth and survival in a competitive market.
- Product marketing focuses on promoting a specific product, while content marketing aims to attract and engage a target audience.
- Crafting a successful product marketing strategy involves market research, product positioning, pricing, branding, distribution, and promotion.
- Product-Led Marketing (PLM) emphasizes using the product itself to drive customer acquisition, activation, and retention.
- Key product marketing metrics include sales revenue, customer acquisition cost (CAC), customer lifetime value (CLV), conversion rates, customer satisfaction, and market share.
- Product marketing managers play a pivotal role in strategizing, executing, and analyzing product marketing efforts.
- A strong understanding of marketing, product development, and sales is essential for a successful product marketer.


